In an era where access to technology is no longer a luxury but a necessity, Africa has been dappling with expensive data and sluggish internet speeds for some time now – contributing to a growing digital divide.
This digital divide (the gap between those who have access to technology and those who don’t) is one of the most persistent 2024 issues facing the continent, with some efforts underway to bridge that gap. As African nations realize it’s the need of the hour to take the initiative and join the Fourth Industrial Revolution, the Kingdom of Kush stands out as a potential pivotal leader in bridging this divide by strategically implementing technology initiatives that empower its citizens and promote inclusive growth.
Understanding the Current Digital Access and Divide

Before delving into solutions, it’s crucial to understand the current state of digital access in Africa. It’s not that Africa isn’t making efforts to bridge the digital divide. However, while progress is being made, disparities remain stark.
Global Investments
Africa is witnessing a surge in investment from tech companies like Google and Facebook parent Meta. These companies are building new data centers and improving internet connectivity across the continent. Google’s new data center in Johannesburg, South Africa is just one example of their commitment to expanding internet access.
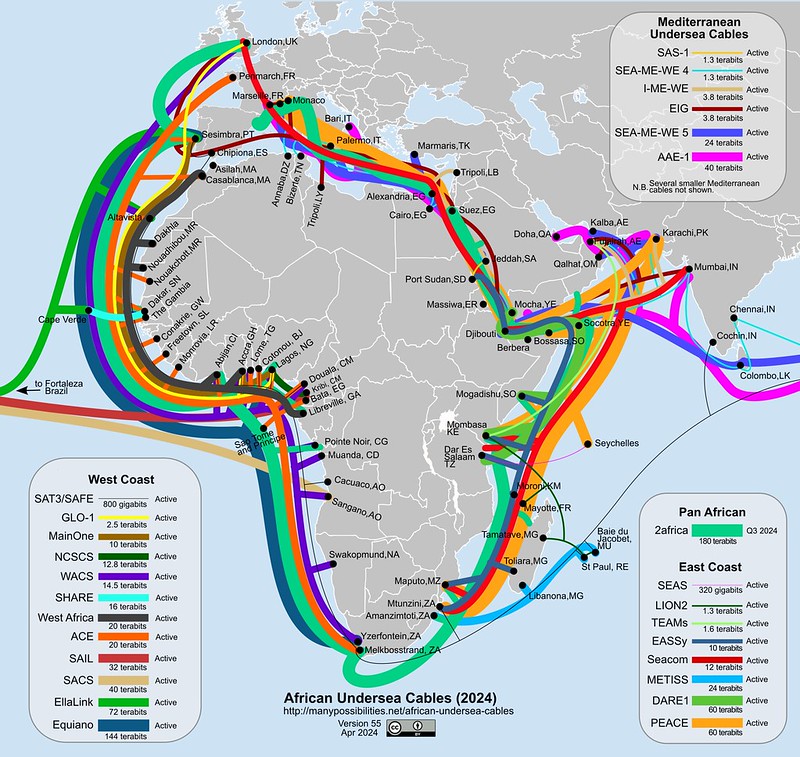
(Source: Submarine Cable Networks)
In 2022, Google invested $1 billion to boost Africa’s digital connectivity. This included building undersea cables like Umoja, which aims to be the first direct fiber-optic link between Africa and Australia. Umoja, one of the projects, will run through several East and Southern African countries, connecting them to a global digital network.
Originating in Kenya, the fiber-optic cable will traverse Uganda, Rwanda, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Zambia, Zimbabwe, and South Africa before extending across the Indian Ocean to Australia.
Uneven Internet Penetration
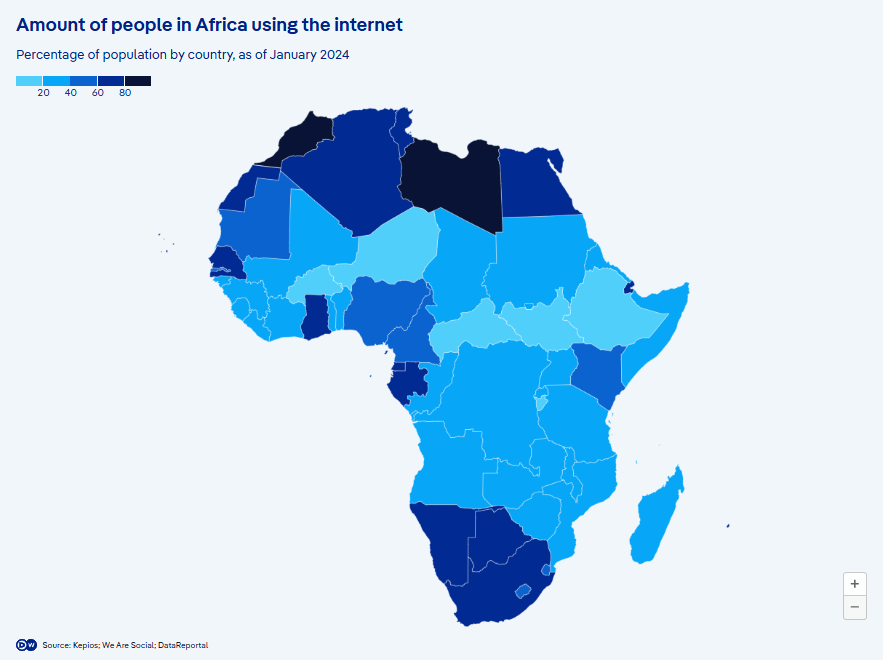
(Source: Deutsche Welle)
Internet access remains uneven across Africa. While Morocco boasts a 90% penetration rate, South Africa lags at 75%. The Central African Republic faces significant challenges, with only 11% of its population online. Ghana, a pioneer in internet adoption, connected in 1992.
High Data Costs
Sub-Saharan Africa’s sky-high mobile data prices are widening the digital divide, leaving millions disconnected. The United Nations Broadband Commission aims to slash these costs by 2025 to ensure everyone can access the internet.
The Kingdom of Kush’s Opportunity

As a newly established nation, the Kingdom of Kush has a unique opportunity to leapfrog traditional development stages and position itself at the forefront of technological advancement in Africa. Here are key strategies and initiatives that Kush may potentially implement to empower our citizens through technology and bridge the digital divide:
1. Develop Robust Digital Infrastructure
- Fiber Optic Network: Invest in a comprehensive fiber optic network that covers both urban and rural areas, ensuring high-speed internet access for all citizens.
- 5G Implementation: Partner with telecommunications companies to roll out 5G technology, providing faster and more reliable internet connections.
- Community Wi-Fi Hubs: Establish free Wi-Fi hotspots in public spaces, schools, and community centers to provide internet access to those who can’t afford personal connections.
- Satellite communication: Provide connectivity to remote areas which also serves as a backup option in case of disruptions to fiber optic or 5G networks.
2. Foster Digital Literacy
- National Digital Literacy Program: Implement a nationwide program to teach basic digital skills to all citizens, regardless of age or background.
- Integration in Education: Incorporate digital literacy and computer science into school curriculums from primary through tertiary levels.
- Mobile Learning Initiatives: Develop mobile apps that teach digital skills, making education accessible even in areas with limited infrastructure.
3. Promote Local Content and Services
- Digital Content Creation Incentives: Offer grants and incentives for local developers and content creators to produce digital content in local languages.
- E-Government Services: Digitize government services to improve accessibility and efficiency, encouraging citizens to engage with technology daily.
- Digital Marketplace: Encourage and assist in creating online marketplaces for local businesses to sell products and services, boosting the digital economy.
4. Implement Affordable Access Initiatives
- Subsidized Devices: Partner with manufacturers to provide low-cost smartphones and tablets to citizens, potentially through a government-subsidized program.
- Data Affordability Measures: Work with telecom providers to offer affordable data packages, including options for low-income families and students.
- Zero-Rating Essential Services: Negotiate with internet providers to offer free access to essential services like education and healthcare websites.
5. Encourage Innovation and Entrepreneurship

- Tech Incubators and Accelerators: Establish innovation hubs and provide support for tech startups, fostering a culture of entrepreneurship.
- Coding Bootcamps: Offer intensive coding programs to rapidly skill up the workforce for the digital economy.
- R&D Investments: Allocate funds for research and development in emerging technologies like AI, blockchain, and IoT.
6. Collaborate Internationally
- Public-Private Partnerships: Engage with global tech companies for infrastructure projects, following the model of Google’s investments in Africa.
- Knowledge Exchange Programs: Establish partnerships with technologically advanced nations for knowledge transfer and capacity building.
- Participation in Global Tech Initiatives: Actively engage in international forums and initiatives focused on bridging the global digital divide.
7. Address Cybersecurity and Digital Rights
- Robust Cybersecurity Framework: Develop comprehensive cybersecurity policies to protect citizens and businesses in the digital space.
- Digital Rights Education: Educate citizens about their rights and responsibilities in the digital world, including privacy and data protection.
- Ethical AI Guidelines: Establish guidelines for the ethical use of AI and other emerging technologies to prevent misuse and discrimination.
8. Focus on Sustainable and Green Technology

- Solar-Powered Internet: Implement solar-powered internet solutions for remote areas, addressing both connectivity and energy challenges.
- E-Waste Management: Develop a comprehensive e-waste management system to handle the increase in electronic devices sustainably.
- Green Data Centers: Invest in energy-efficient data centers powered by renewable energy sources.
Overcoming Challenges
While these initiatives offer immense potential, the Kingdom of Kush is also focusing on addressing several challenges:
- Resource Allocation: Balancing the need for digital investment with other pressing national priorities.
- Cultural Adaptation: Ensuring that technological advancements respect and integrate with local cultural norms and practices.
- Digital Inequality: Preventing the creation of new forms of inequality as technology advances.
The Path Forward

As a nation moves forward, we aim to uncover unprecedented opportunities for our citizens, drive economic growth, and contribute to the broader development of the African continent.
As we look to the future, the potential for transformation is immense. We are confident that the Kingdom of Kush will seize this digital moment and lead the way in creating a more connected, empowered, and prosperous Africa.
What are your thoughts on these strategies? How do you think the Kingdom of Kush can best use technology for its development? Share your ideas in the comments below or spread the word about Kush’s digital ambitions by sharing this post!



